Why refraction occurs?
Refraction occurs because there is a change in velocity between both medium.
Refractive index
Refractive index can be defined as a constant that gives the degree to which refraction or bending of a wave takes place between the two medium.
Here are the formulas associated with refractive index:
- Snell's Law
- n = incident velocity ÷ refractive velocity
- n= incident wavelength ÷ refractive wavelength
n => refractive index
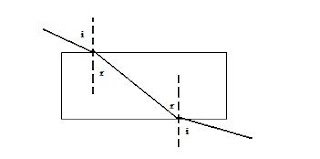
i => angle of incidence
r => angle of refraction
- anb = 1 / bna
'a' and 'b' are the different mediums.
Where do waves bend with respect to the normal?
When waves are entering a denser medium they bend toward the normal but when entering a less dense medium they bend away from the normal.
What happens to light when it meets a boundary perpendicularly?
Refer to the diagrams below. When the wave meets the boundary perpendicularly it is not diffracted it just goes straight through.